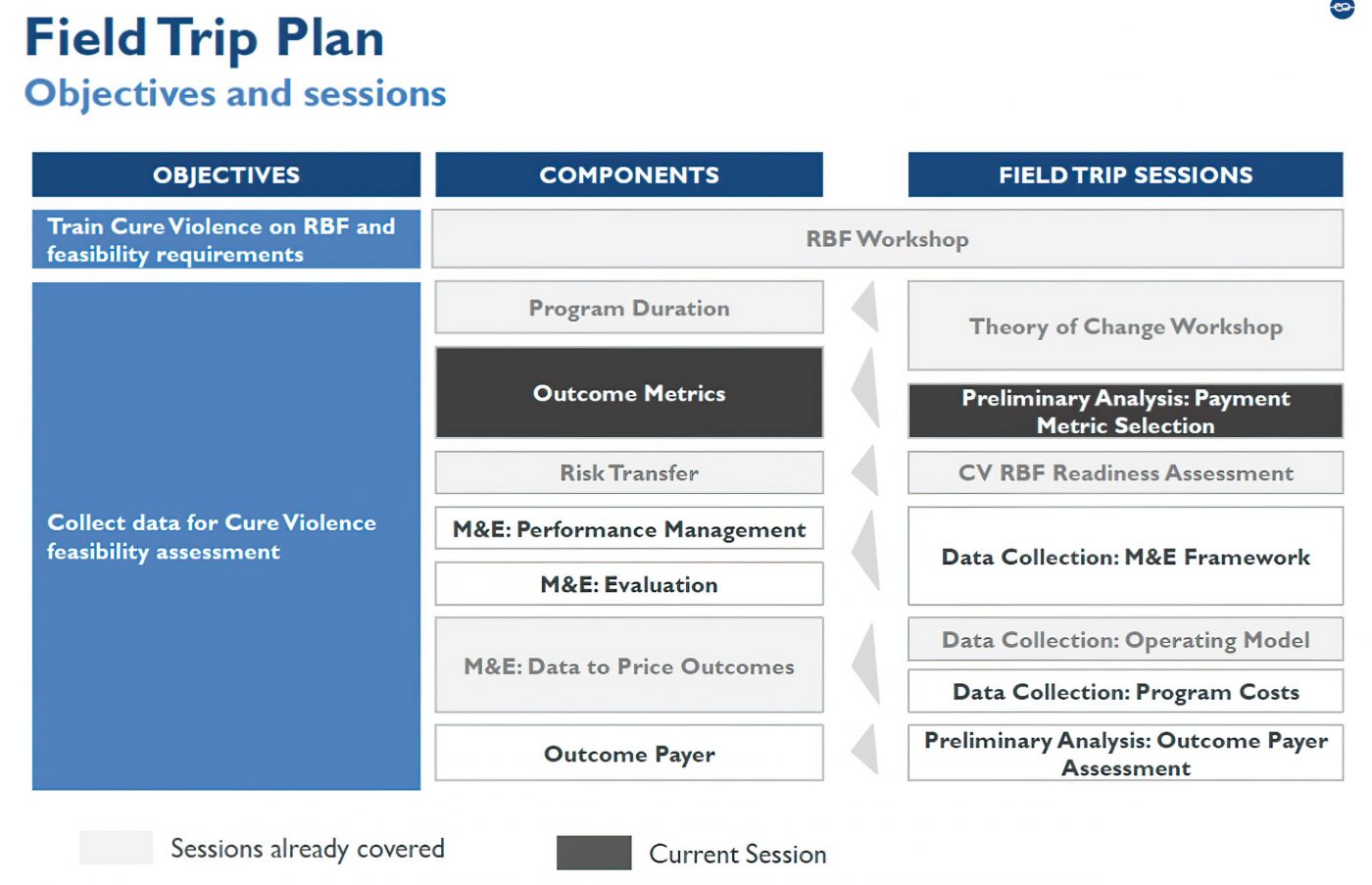
Instiglio conducted a feasibility study to assess how Cure Violence could implement its intervention in Chihuahua, Mexico using Results-Based Financing (RBF) to increase its impact and reach. And included:
1. An RBF training was conducted with Cure Violence staff to highlight the potential value add of RBF for Cure Violence programming.
2. Assessment of common RBF mechanisms and determine if/how such RBF mechanisms are suitable for the Cure Violence program in Mexico.
3. Recommendations to prepare Cure Violence’s program for RBF funding.
4. Identification and high-level assessment of potential funders for a Cure Violence RBF mechanism.
Country
Mexico
Timeline
2016 – 2017
Type of Project
Feasibility study
Sector
Community anti-violence
public safety & health
project description
Across the globe, violence affects and sadly takes the lives of many. Particularly in large, urban areas, and especially among youth, violence is commonly a byproduct of those engaging in illicit activities, but various factors can be attributed to the issue.
Chihuahua is one of the most violent cities in Mexico, where 90% of violent deaths are due to organized crime. As such, there have been substantial efforts by multiple public, private, and citizen organizations to deter violence. Nevertheless, since 2015 the epidemic of violence in Chihuahua has risen, mainly attributable to the growing conflict between drug cartels over the control of sales and distribution channels.
Cure Violence is an international NGO implementing its community-based approach in Chihuahua, approaching violent behavior as a public health issue that spreads through communities as epidemic diseases do. Thus, by implementing disease control strategies, Cure Violence works to address violent behavior and curbs its transmission. This work is done under three main pillars, in partnership with local and validated organizations and individuals in the community:
- Detect and interrupt the transmission of violence: Anticipate where violence may occur and intervene before it erupts.
- Change the highest potential transmitters’ behavior: Identify those at the highest risk for violence and work to change their behavior.
Change community norms: Influence social norms to discourage the use of violence.
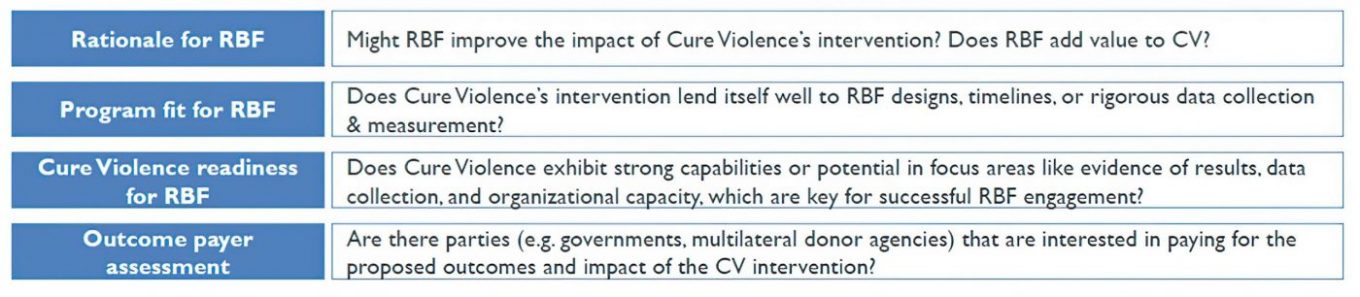
Instiglio worked with Cure Violence conducting a feasibility study to assess how they could implement its intervention in Chihuahua using Results-Based Financing (RBF) mechanisms as a means to increase its impact and reach. This included an RBF training to Cure Violence staff, including international examples of those models, and explaining how they add value to social programs, and a preliminary assessment of common RBF mechanisms (e.g., development impact bond (DIB), performance-based contract) as suitable fits for the Cure Violence program in Mexico. In its assessment, Instiglio’s feasibility study also provided recommendations to improve Cure Violence’s readiness for RBF and helped Cure Violence identify potential outcome payers for such a mechanism.
Despite a significant reduction in violence 2012,¹ there has been an increase in homicide rates since 2016 at both the state and municipal levels.² it is estimated that deaths by shooting is the main reason for the decline in life expectancy among men aged 15 to 75.³
Graph I.Juarez City Homicides Rates,2016
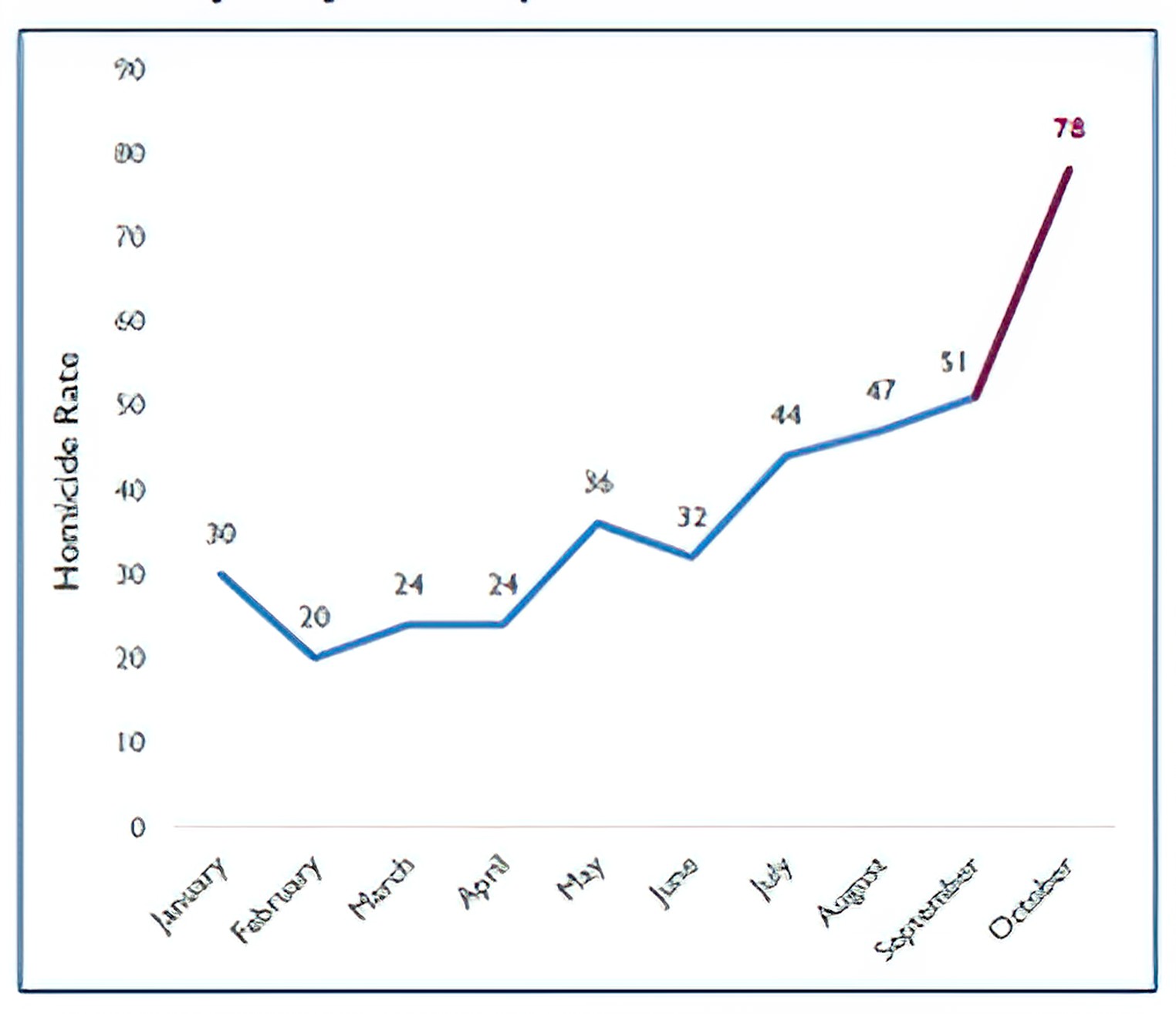
Graph 2. Chihuahua State Homicides Rates,2016
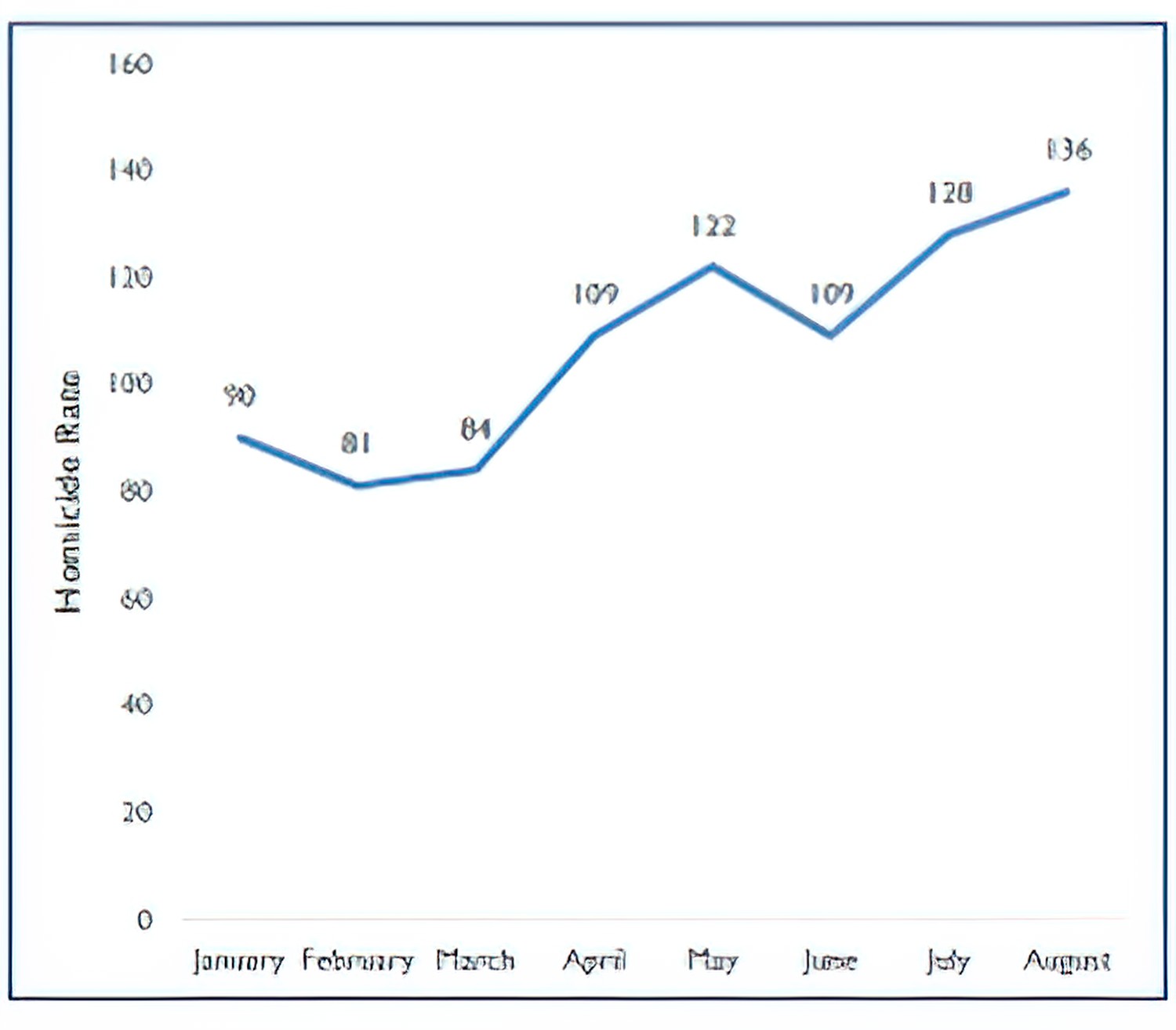
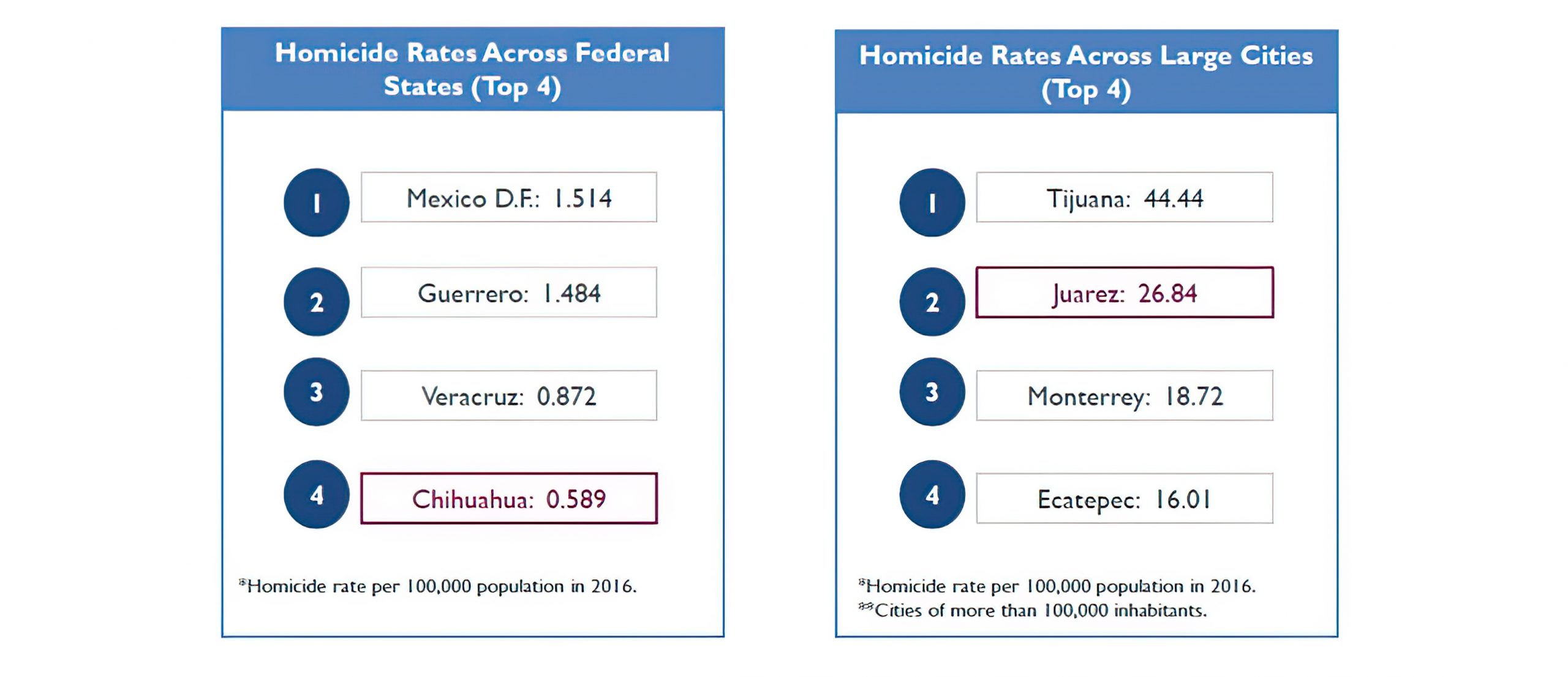
¹Caldero,Felipe. “Todos Somos Juarez: An Innovative Strategy to Tackle Violence and Crime.” Latin America Policy Journal. Harvard Kennedy School of Government, 2013.
²Juarez Citizen Observation and SNSP.
³Lopez, Vega, and Maria Guadalupe. “Violence, Firearms and Life Expectancy in Mexico.” Isaconf,2016.


