Instiglio worked with UNICEF and the Government of Uganda to identify and define an innovative financing strategy that could have a large and sustained impact on the sanitation sector of the country. The steps to defining the innovative financing strategy involved a review of the social sector to identify best-fit opportunities and an analysis of the sanitation sector in Uganda, including the different stakeholders that would be involved in the strategy. With this information, a blended finance mechanism proposal with the ability to crowd additional private capital to the sanitation sector was developed.
Country
Uganda
Timeline
2019-2020
Type of Project
RBF Design or Implementation
Sector
Sanitation
project description
The challenge: In Uganda, sanitation services are limited and vary immensely between rural and urban areas. Only 19% of Uganda’s population has access to basic sanitation services (WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2019), diarrhea is one of the top death in children, and economic losses for premature deaths associated to poor sanitation and hygiene are estimated to cost US$147 million each year. According to the World Bank estimates, achieving national sanitation targets will require between 5 to 9 times the current level of investment. Besides, there is not enough government ownership on the topic; at least 3 ministries have mandates in sanitation but limited funding translates into unclear priorities, responsibilities, and accountability for performance.
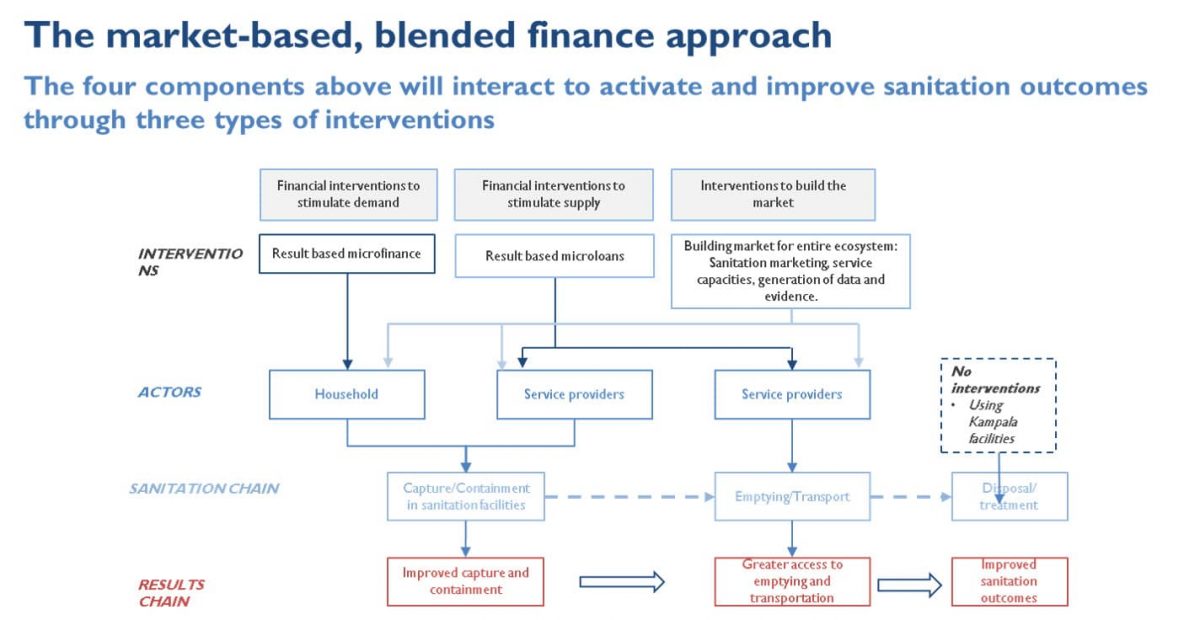
To support improved outcomes in Uganda’s sanitation sector, Instiglio and UNICEF developed an innovative financing strategy that promoted both efficiency and additionality of resources targeted towards sanitation. To support implementation of the strategy, a detailed analysis was conducted on the optimal sub sectors where an innovative financing pilot could be rolled out through supporting private service providers and utilizing blended financing modalities.

The key components of the innovative financing strategy included:
- Strategic launch sites: Selecting geographies where a market-based initiative would prosper
- Demand creation strategy: Setting initiatives to support the expansion of household demand in order to attract private capital were set. A Concessional Microfinance system and Sanitation campaigns were put in place
- Service and supply strategy: Leveraging the existing treatment facilities and building the capacity of service providers
- Financing strategy: Proposing blended Finance to support households and providers and result based financing in all financing streams
By focusing on strengthening the demand, the supply and the market of the sanitation sector in Uganda, the project aimed to improve the conditions of the social sector of the country. Ultimately, it had the purpose of improving the capture and containment of sanitation facilities, generating greater access to emptying and transportation and the ameliorating sanitation outcomes.
A phased approach to implementing this strategy is recommended, it will require committed champions within the government and its partners, a collaborative approach between sanitation stakeholders (funders, NGOs, experts, providers), and a discovery mindset.